A Structured Approach to Options Trading Strategies
Options trading is one of the most versatile areas of financial markets, allowing traders to hedge, speculate, and manage risk effectively. However, the abundance of strategies and nuances can often feel overwhelming. This article provides a structured approach to classifying and understanding options and trading strategies.
We can simplify decision-making and enhance trading performance by organizing strategies into categories based on market bias, volatility expectations, and risk tolerance.
The Framework
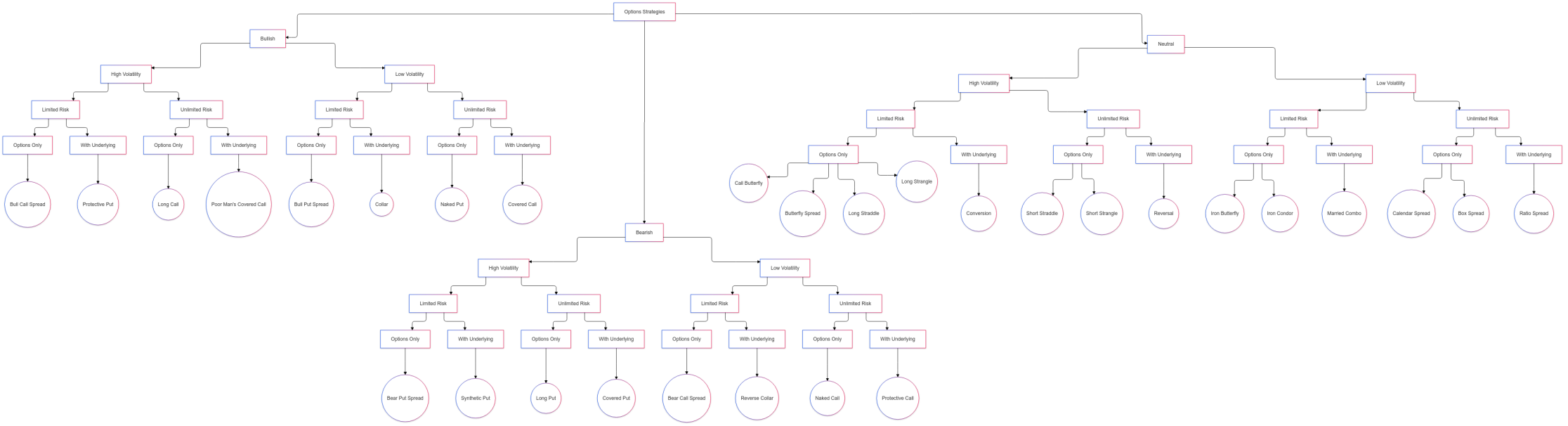
Options strategies can be broadly classified into three major categories:
- Bullish Strategies: For markets expected to move upward.
- Bearish Strategies: For markets expected to decline.
- Neutral Strategies: For markets expected to remain range-bound or exhibit low directional movement.
Each category is further divided based on:
- Volatility Expectations: High or Low Volatility
- Risk Exposure: Limited or Unlimited Risk
- Instrument Composition: Options Only or Combined with the Underlying Asset
It is essential to clarify the meaning of unlimited risk within the context of this classification. In this framework, "unlimited risk" does not imply recklessness or a complete lack of safeguards. Instead, it simply refers to strategies where the trader must actively manage the risk themselves rather than having a predefined cap on potential losses. For example, selling naked calls or puts exposes a trader to theoretically unlimited or substantial losses if the market moves dramatically against the position. However, with proper risk management techniques—such as setting stop-loss levels, dynamically adjusting positions, or hedging with other instruments—traders can effectively control their exposure and mitigate downside risks.
This distinction is crucial, as many "unlimited risk" strategies can still be executed responsibly and form part of a sound trading plan. Understanding that the trader is responsible for managing these risks allows for greater flexibility and customization in adapting to different market conditions. It also highlights the importance of vigilance and discipline when employing such strategies, ensuring they align with your overall risk tolerance and trading objectives.
Below, I break down each category in detail, highlighting specific strategies.
1️⃣ Bullish Strategies
These strategies aim to profit from upward price movements in the underlying asset. They vary in complexity, capital requirements, and risk exposure.
High Volatility
Limited Risk:
-
Bull CALL Spread (Options Only): A debit strategy using two CALL options—buying a CALL at a lower strike and selling another at a higher strike. It offers limited risk and limited reward.
-
Protective PUT (With Underlying): Combines ownership of the underlying asset with a PUT option for downside protection.
Unlimited Risk:
-
Long CALL (Options Only): Buying a CALL option to capture upside potential, with the maximum loss limited to the premium paid.
-
Poor Man's Covered CALL (With Underlying): Uses LEAPS (long-term equity anticipation securities) as a cost-efficient alternative to a traditional covered CALL.
Low Volatility
Limited Risk:
-
Bull PUT Spread (Options Only): Involves selling a higher-strike PUT and buying a lower-strike PUT to profit from modest price increases or stability.
-
Collar (With Underlying): This strategy protects a long stock position by combining a protective PUT and a covered CALL.
Unlimited Risk:
-
Naked Put (Options Only): Selling an uncovered PUT to generate income but exposes you to significant downside if the stock drops.
-
Covered CALL (With Underlying): Writing CALL options against owned stock, generating income at the cost of capping upside potential.
2️⃣ Bearish Strategies
These strategies are ideal when anticipating a decline in the underlying asset.
High Volatility
Limited Risk:
-
Bear PUT Spread (Options Only): Combines buying a PUT and selling a lower-strike put to create a defined-risk bearish position.
-
Synthetic PUT (With Underlying): Mirrors the payoff of a long put by combining a short stock position with a long CALL.
Unlimited Risk:
-
Long PUT (Options Only): Buying a PUT option to profit from sharp declines.
-
Covered PUT (With Underlying): A short stock position paired with a written PUT option, exposing you to unlimited risk if prices rise sharply.
Low Volatility
Limited Risk:
-
Bear CALL Spread (Options Only): Involves selling a lower-strike CALL and buying a higher-strike call to profit from modest price declines.
-
Reverse Collar (With Underlying): A bearish adaptation of the collar strategy for downside protection.
Unlimited Risk:
-
Naked CALL (Options Only): Selling uncovered CALLs to earn premiums, with exposure to unlimited losses.
-
Protective CALL (With Underlying): This strategy combines a short stock position with a CALL option for upside protection.
3️⃣ Neutral Strategies
Neutral strategies are designed for markets expected to trade within a range or experience limited directional movement. These strategies often rely heavily on implied volatility and time decay.
High Volatility
Limited Risk:
-
Butterfly Spread: A multi-leg strategy that profits from minimal price movement around the central strike.
-
Long Straddle/Strangle: Buying both CALLs and PUTs to profit from significant price movements in either direction.
Unlimited Risk:
- Short Straddle/Strangle: Selling both CALLs and PUTs to collect premiums, but with exposure to significant risks if prices move dramatically.
Low Volatility
Limited Risk:
-
Iron Butterfly/Condor: A combination of spreads that profits from low volatility, with clearly defined risk and reward.
-
Box Spread: A synthetic risk-free strategy exploiting mispricing between CALLs and PUTs.
Unlimited Risk:
- Calendar Spread: Combines short-term and long-term options to profit from stable prices and differences in time decay.
Why This Framework Matters
Understanding the classification of options strategies is not just theoretical—it's highly practical. Here's why:
-
Tailored Decision-Making: Aligning strategies with your market view ensures consistency in your trading approach.
-
Risk Management: By knowing each strategy's risk/reward profile, you can better plan your capital allocation.
-
Volatility Adaptation: Options allow you to profit from quiet and turbulent markets, provided you select the right strategy.
Visual Flowchart
I've created a visual flowchart outlining this classification system to simplify the relationships between these strategies.
Final Thoughts
Options trading is an art and a science. The ability to select and implement the right strategy tailored to market conditions and your objectives sets successful traders apart. Whether you're a beginner exploring the basics or an advanced trader refining your edge, this structured approach will help you navigate the complexity of options markets.
💬 What's your approach to options trading?
Let's discuss in the comments! Share your go-to strategies, experiences, or challenges—I'd love to learn from your perspectives. 🚀
Note: This article is for educational purposes only. Options trading involves significant risk. Consult with a qualified financial advisor before implementing any investment strategy.